Manufacturing ERP is a centralized platform for monitoring all business operations and processes. Its inbuilt modules and shared database allow manufacturers to streamline the supply chain, quality assurance, and operations across all departments. The manufacturing sector uses two basic production processes: discrete and process.
What is Discrete Manufacturing?
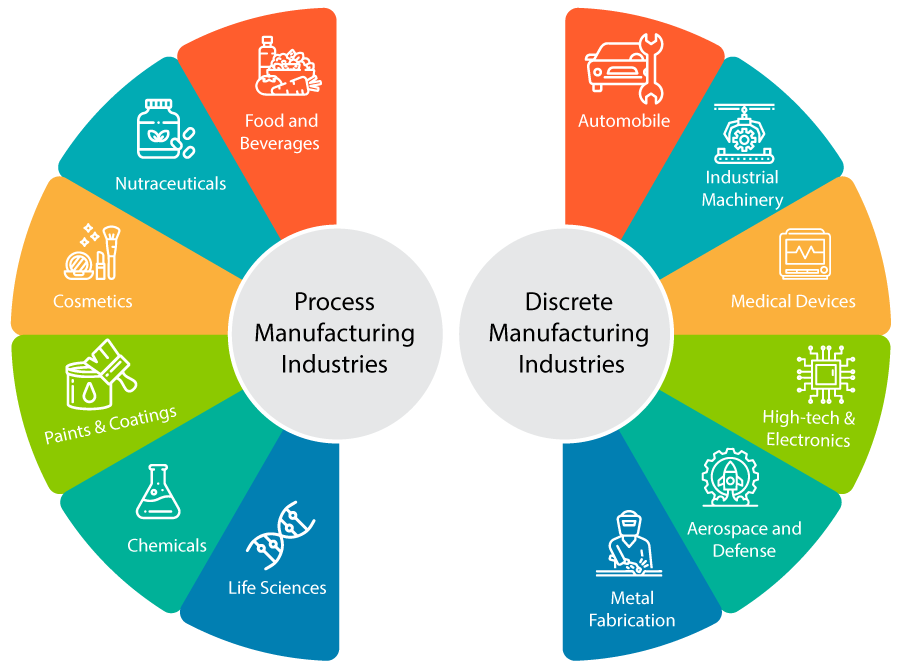
Discrete manufacturing: This approach produces low-volume items in individual units or batches. Items produced in discrete manufacturing are easily identifiable and can be disassembled. Manufacturing industries that come under discrete manufacturing include:
Key features of discrete manufacturing:
- Parts, assemblies, and unit production: Each component and part can be tracked individually.
- Bill of Materials (BOMs): A comprehensive list of materials, components, and sub-assemblies required to manufacture the final product.
- Items can be customized and modified based on customer specifications.
- It includes make-to-stock, make-to-order, and assemble-to-order production.
- Discrete manufacturing involves assembling, joining, attaching, and fixing products.
What is Process Manufacturing?
Process manufacturing involves producing goods by combining supplies, ingredients, or raw materials based on a recipe or formula. This approach mainly produces goods in bulk, and raw materials cannot be disassembled in their original form.
Process manufacturing is a production method in which goods are created by combining supplies, ingredients, or raw materials using a predetermined formula or “recipe.” The approach is frequently employed in industries where goods are produced in bulk. Process manufacturing industries include:
Key features of process manufacturing:
- Continuous or batch production
Goods are produced in large quantities. Items are made either in a continuous process or batch-based processes.
- Quality control and consistency
Quality control measures are necessary for meeting strict quality standards at every production stage. This includes stringent monitoring of ingredients, proportions, and conditions.
- Regulatory compliance
Product safety and regulations are paramount, and they differ for each industry—chemicals, food, and beverage, etc.
Discrete Manufacturing vs. Process Manufacturing
Let’s have a quick look at the differences between discrete and process manufacturing ERP.
| Discrete Manufacturing | Process Manufacturing | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Production | Individual items are manufactured with assembly lines | Bulk quantity is produced |
| BOM or Recipes | Bill of Material (BOM) | Recipes/formulas are used |
| Customization | High scope of product customization | Limited customization is done |
| Quality Control | Quality check is done on individual production | Quality check is done across batches |
| Material Used | Solids | Liquid, Powder, or Gas |
What is the best ERP software choice for you?
ERP selection is a time-consuming and challenging task. It involves exploring different options, attending demos, and finding the best fit for your business. Choosing ERP software depends on many aspects: type of production (bulk production or production of individual items), customization, quality control, complexity of production processes, and more.
Before selecting ERP software for your manufacturing company, assess your processes—whether you produce unique items in batches or run continuous production lines. Regulatory compliance also plays a significant role in deciding between discrete and process manufacturing software. It is better to consider your business’s product configurations and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Discrete manufacturing ERP software focuses on managing individual components, BOM, routing, and assembly processes. Process manufacturing ERP software focuses on batch production, regulatory compliance, and formula management. Both ERP software solutions are designed for better efficiency, improved resource planning, and better quality control, but their functionality differs based on the above-mentioned factors.
Due to these fundamental differences, a discrete manufacturing software may lack the necessary features, record keeping, and flexibility to support the unique needs of process manufacturers in the food, chemical, nutraceutical, or life sciences industries effectively. Therefore, it is important that manufacturers in these industries invest in software specifically designed for process manufacturing, like BatchMaster Software solutions, to optimize their operations and remain compliant with industry regulations.
About BatchMaster ERP
BatchMaster process manufacturing ERP is an industry-specific solution that offers cloud and on-premise modules for growing small to mid-size recipe- and formula-based manufacturers. BatchMaster ERP is designed with industry-specific functionality, libraries, and templates. Our experienced implementation team gets BatchMaster up and running quickly and effectively, maximizing your time to value.
Want to see BatchMaster ERP in action? Watch our video or schedule a free demo today.