What is Process Manufacturing?
EXAMPLES OF PROCESS MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIES

Food Manufacturers
The food industry is made up of several segments, including bakery, beverage, dairy, dressings & sauces, flavors & additives, seasonings, and prepared foods. All these industry segments are subject to strict regulatory mandates that require the identification and labeling of ingredients (FDA nutritional fact panels), meeting label claims, as well as tracking and tracing of all raw materials and finished goods in a production job. In addition to food safety concerns, food manufacturers must properly manage product expiration dates, shelf lives, various quality grades, by-products, and co-products.

Chemical Manufacturers
The chemical industry is made up of several segments, including paints and coatings, adhesives and sealants, personal care and cosmetics, fragrances, and other specialty chemicals. All these industry segments are all subject to strict regulatory mandates that require the identification and labeling of products (GHS / SDS) that pose a health and safety risk due to exposure, inhalation, and ingestion, as well as being explosive and flammable. In addition to hazmat concerns, chemical manufacturers must properly manage product variable characteristics, such as strength, density, and active vs filler ingredients.

Nutraceuticals Manufacturers
The nutraceutical industry is made up of several segments, including dietary and sports supplements, vitamins and minerals, and herbal remedies. All these industry segments are all subject to strict regulatory mandates that require the identification and labeling of products (FDA supplemental panels), meeting label claims, as well as tracking and tracing of all raw materials and finished goods in a production job. Nutra manufacturers must properly manage all product types, including capsules, soft gels, and tablets. They must also capture and report on all manufacturing steps from formulation through production.

Life Sciences Manufacturers
The life sciences industry is made up of several segments, including generic / OTC drugs enzymes and specialty biologics. All these industry segments are subject to strict regulatory mandates that require the identification and labeling of products, meeting label claims, as well as the tracking and tracing of all raw materials and finished goods in a production job. In addition to effectively managing product types, life sciences manufacturers must provide electronic signatures and audit trail reports to CGMP auditors. In addition, they must validate their processes.
A FEW DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROCESS MANUFACTURING
VS DISCRETE MANUFACTURING
INDUSTRY CHALLENGES THAT A PROCESS MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE CAN SOLVE

Batch Consistency
Product Recalls


Ingredient Management
Regulatory and Compliance Management

FEATURES OF A PROCESS MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE
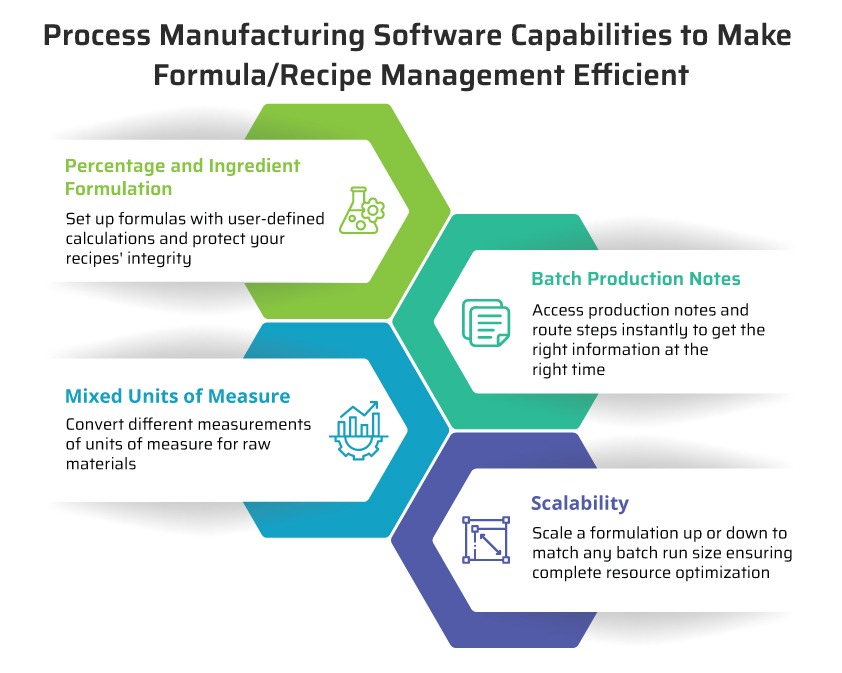
A FEW ADVANTAGES OF PROCESS MANUFACTURING SPECIFIC SOFTWARE

Units of Measure
An item may have multiple units of measures defined and require conversion from purchasing to inventory to manufacturing to ordering to shipping units of measures. In addition, an item may need to be converted from weight to volume units or vice versa, using a specific density. This is while simultaneously allowing the item to be used in each UOM.

Formulation
In process manufacturing, intermediates and finished goods are created by defining their components, quantities, and units of measure, as well as QC tests and instructions, costs, and co and by-products. Advanced formulation provides visibility to physical and nutritional target property values and the generation of industry-compliant documents and labels.

Lot Traceability and Recall
Lot management involves the capture and generation of lot numbers for raw materials and finished goods inventory, from receiving into production through shipping. The ability to track and trace the lineage of all raw materials and finished products by lot number, then generate recall letters is a mission-critical function for process manufacturers quickly and easily.

Expiration Date
Product expiry dates, as well as its shelf life, can be captured or calculated. This is then considered when allocating raw material inventory for a batch job or finished good inventory for a sales order.
Quality
With a high level of variability associated with inventory conditions, a variety of quality statuses can be applied to raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods. This is in the receiving, production, and order fulfilment processes.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT SYSTEM FOR YOUR PROCESS
MANUFACTURING BUSINESS?
BatchMaster Manufacturing Software for Process Manufacturers
With a software architecture built from the ground up for process manufacturers, we recommend you learn more about our add-on process manufacturing application for QuickBooks, Sage 100 & 300, Microsoft Dynamics GP and SAP Business One, or our end-to-end, industry-specific ERP solution.